General Project Plan of Japan Natural Gas Pipeline
The consumer price of natural gas in Japan is more than double, comparing with international price levels, because Japan has long term LNG purchase contracts as "Take or Pay" bases. And its country is far isolated from the continents and it was considered to be difficult to establish piepeline networks offering reasonable price gas sypply.
This project is able to break such current stagnated business structures, and it might be trigger to stimulate deregulations of the energy supply business.
This project is in a strong position to proceed, comparing to other plans, as this can be started by the agreements between Japan, Russia and major oil companies, being free from tough multi-country negotiations. The most advantageous merit are to treat abundant russian gas reserves for 100 years, initially from Sakhalin Island and later from East Siberian regions, by the pipeline systems. This realization results in offering stable & cheap price gas like coals and oils in entire Japanese territory.
Natural gas supplying routes to specifiec regions are:
- Metropolitan Area Pacific Route
- Center & West Industrial Areas Japan Sea Route
- Tokai Area Pacific Route
- Sikoku, Kyushu Areas Japan Sea Route
Different from batch systems with LNG carriers, this completion can bring about the establishing the commodity gas market in Japanese economy systems, expanding LNG storage capacities.
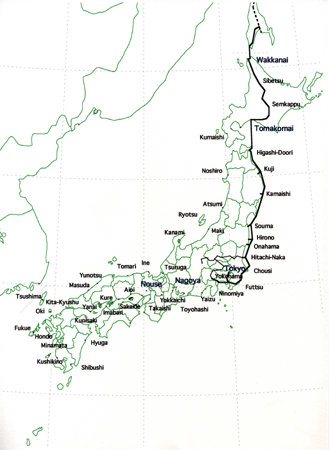 Phase 1 Goal (2006AD)
Phase 1 Goal (2006AD)
- Max. 2,000t/hr natural gas transporting to Hokkaido, Tohoku, and to Tokyo areas from Sakhalin Island
Phase 1 General
- Piping Specification and Station Settlement
- On-Land Pipeline Transport in Hokkaido
- Offshore Pipeline Transport in Other Areas
Gas Transprt Quantity in Hokkaido Trunkline 2,000t/hr
- Demand in Hokkaido 300t/hr
Gas Transprt Quantity in Pacific Route 1,700t/hr
- Demand in Tohoku 500t/hr
- Demand in Kanto 400t/hr
- Demand in Tokyo 700t/hr
- Demand in Tokai 100t/hr
Trunkline Specifications are: (Shown in Black)
Hokkaido Trunkline 1,422mmOD x 7.5MPa
Tohoku Region in Pacific Route 1,321mmOD x12.0MPa
Kanto region In Pacific Route 1,321mmOD x12.0MPa
Tokyo region in Pacific Route 1,422mmOD x 7.0MPa
Tokai region in Pacific Route 1,422mmOD x 7.0MPa
Booster Stations are:
Hokkaido Trunkline 2 St.
Tohoku region in Pacific Route 1 St.
Kanto refion in Pacific Route 0 St.
Tokai region in Pacific Route 0 St.
 Phase 2 Goal (2013AD)
Phase 2 Goal (2013AD)
- Max. 3,400t/hr natural gas transporting to Hokkaido, Tohoku, and to Tokyo areas from Sakhalin Island and East Siberia
Phase 2 General
- No Additional Trunklines
- Booster Stations in Hokkaido
- Booster Stations in Pacific Route
Gas Transprt Quantity in Hokkaido Trunkline 3,400t/hr
- Demand in Hokkaido 300t/hr
Gas Transprt Quantity in Pacific Route 3,100t/hr
- Demand in Tohoku 700t/hr
- Demand in Kanto 700t/hr
- Demand in Tokyo 1,400t/hr
- Demand in Tokai 300t/hr
New Trunkline Specifications are:
Hokkaido Trunkline None
Tohoku Region in Pacific Route None
Kanto region In Pacific Route None
Tokyo region in Pacific Route None
Tokai region in Pacific Route None
Additonal Booster Stations are:
in Hokkaido Trunkline 3 more St.
Tohoku region in Pacific Route 1 more St.
Kanto refion in Pacific Route 1 more St.
Tokai region in Pacific Route 0 St.
 Phase 3 Goal (2020AD)
Phase 3 Goal (2020AD)
- Max. 6,900t/hr natural gas transporting to Hokkaido, Tohoku, Tokyo and to Nagoya & Osaka areas
Phase 3 General
- Identical Trunkline Installment in Hokkaido
- Offshore Pipeline Transport in Japan Sea Route
- On-Land & Offshore Pipeline in Tokai region
- Connecting Pipeline for Pacific & Japan Sea Routes
Gas Transprt Quantity in Hokkaido Trunkline 6,900t/hr
- to Hokkaido 500t/hr
Gas Transprt Quantity in Pacific Route 3,900t/hr
- to Tohoku 700t/hr - to Kanto 800t/hr
- to Tokyo 1,700t/hr - to Tokai 700t/hr
Gas Transprt Quantity in Japan Sea Route 2,500t/hr
- to Japan Sea 700t/hr - to Nagoya 700t/hr
- to Osaka 900t/hr - to Seto Sea 200t/hr
New Trunkline Specifications are: (Shown in Red)
Hokkaido Trunkline 1,422mmOD x 7.5MPa
Tokai region in Pacific Route 1,422mmOD x 7.0MPa
Japan Sea In Japan Sea Route 1,321mmOD x12.0MPa
Nagoya region in Japan Sea Route 1,219mmOD x 7.0MPa
Seto Sea in Japan Sea Route 1,067mmOD x 7.0MPa
San-In region in Japan Sea Route 1,219mmOD x 10.0MPa
Additonal Booster Stations are:
Tohoku region in Pacific Route 4 more St.
Kanto region in Pacific Route 2 more St.
Tokai region in Pacific Route 3 St.
Japan Sea in Japan Sea Route 4 St.
 Phase 4 Goal (2030AD)
Phase 4 Goal (2030AD)
- Max. 10,000t/hr natural gas transporting to Whole the Japanese territory
Phase 4 General
- Identical Trunkline Installment in Hokkaido
- Offshore Pipeline Transport in San-In & Kyushu
- Med-Pressure Offshore Pipeline in Seto Sea region
Gas Transprt Quantity in Hokkaido Trunkline 10,000t/hr
- to Hokkaido 600t/hr
Gas Transprt Quantity in Pacific Route 4,800t/hr
- to Tohoku 700t/hr - to Kanto 1,100t/hr
- to Tokyo 2,200t/hr - to Tokai 800t/hr
Gas Transprt Quantity in Japan Sea Route 4,600t/hr
- to Japan Sea 800t/hr - to Nagoya 900t/hr
- to Osaka 1,200t/hr - to Seto Sea 800t/hr
- to Kyushu 900t/hr
New Trunkline Specifications are: (Shown in Magenta)
Hokkaido Trunkline 1,422mmOD x 7.5MPa
Seto Sea in Japan Sea Route 1,067mmOD x 7.0MPa
East-Kyushu In Japan Sea Route 914mmOD x 7.0MPa
San-In region in Japan Sea Route 1,067mmOD x10.0MPa
West-Kyushu in Japan Sea Route 1,067mmOD x10.0MPa
Additonal Booster Stations are:
Tohoku region in Pacific Route 4 more St.
Kanto region in Pacific Route 1 more St.
Japan Sea in Japan Sea Route 2 more St.
Seto Sea in Japan Sea Route 2 more St.
to Gas Flow Design Page
 Phase 1 Goal (2006AD)
Phase 1 Goal (2006AD) Phase 2 Goal (2013AD)
Phase 2 Goal (2013AD) Phase 3 Goal (2020AD)
Phase 3 Goal (2020AD) Phase 4 Goal (2030AD)
Phase 4 Goal (2030AD)