Gas Flow Design Result: Phase 4
In Phase 4 (Final Phase), Japan Pipeline system must be completed by extending Japan Sea Route into Sikoku and Kyushu sections. The gas to Sikoku and East Kyushu sections is to be supplied via Seto Sea line, and the natural gas to West Kyushu via SanIn line.
Another additional 1,422mmOD x 7.5MPa on-land piping is installed in Hokkaido. Resultant 3 trunklines of 1,422mmOD are to be world biggest natural gas pipeline system.
The offshore trunkline sized according to same specifications as on-land pipings of 7.0MPa in Seto Sea shall be extended to Sikoku sections and to Shibushi, southern end of East Kyushu.
The maximum pressure in SanIn offshore trunkline is settled at 10.0MPa, less figure than that in Japan Sea coastline, due to less flow rate. This line shall be extended to Kushikino via northern remote islands, southern end of West Kyushu.
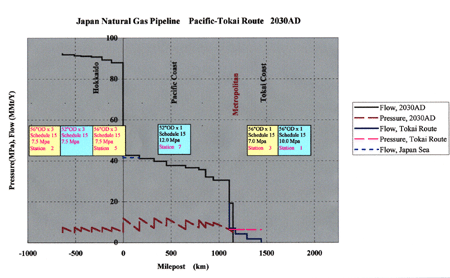 Gas Transport in Hokkaido 10,000t/hr
Gas Transport in Hokkaido 10,000t/hr
- Hokkaido 600t/hr
Gas Transport in Pacific Route 4,800t/hr
- Tohoku 700t/hr - Kanto 1,100t/hr
- Tokyo 2,200t/hr - Tokai 800t/hr
Although another trunline is installed, 5 booster stations are remained same as former Phase period, except for increased numbers of compression units.
The addition of 2 stations is needed to secure the required flow rate, in Pacific Route. The total station number shall be 8.
3 booster stations installed in Tokai region of Pacific Route might be unnecessary to be in service during normal mode. And compression units in these stations are to be up in the only emergency cases of securing back-up capacity, same as in Phase 3.
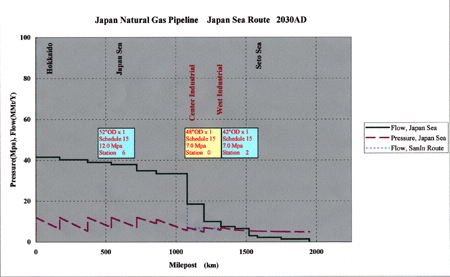 Gas Transport in Japan Sea 4,600t/hr
Gas Transport in Japan Sea 4,600t/hr
- Japan Sea 800t/hr - Nagoya 900t/hr
- Osaka 1,200t/hr - Seto Sea 800t/hr
- Kyushu 900t/hr
The flow rate of Phase 4 in Japan Sea Route reached to rated figure, and the flow design is settled by total 6 booster station system, adding 2 stations.
2 stations are needed in Seto region of Japan Sea Route.
No boosters are necessary in SanIn and Kyushuu regions of Japan Sea Route.
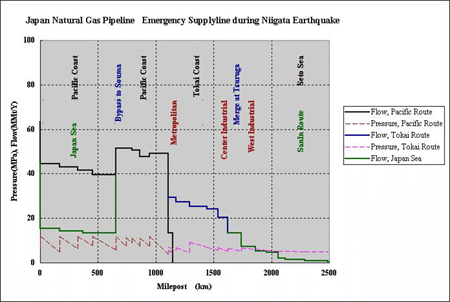 During emergency, for example, by Niigata earthquake accident, the gas delivery to Nagoya and Osaka areas can be secured via Pacific Route.
During emergency, for example, by Niigata earthquake accident, the gas delivery to Nagoya and Osaka areas can be secured via Pacific Route.
Bypassing Niigata region, natural gas in Japan Sea Route shall be merged to Pacific Route via Atsumi - Souma connecting line and transported to Nagoya by using Tokai back-up line.
That line is merged to Japan Sea Route via Nagoya - Tsuruga connecting line. And delivery to Osaka area and downstream regions are to be supplied in normal Japan Sea Route.
Due to the limited capacity of Pacific Route, 72% delivery to whole the Japanese regions might be expected in Phase 4 stage.
The batch recovery system used in Phase 1 &2 is applicable to Niigata area.
"Emergency cases are not limited to the accident like the earthquake in Niigata area."
" The flow design analyses concluded that the back-up system could be applicable in the case of the emergency occurance in other areas like Pacific North, Japan North, Tokai regions."
Back to Top Page
 Gas Transport in Hokkaido 10,000t/hr
Gas Transport in Hokkaido 10,000t/hr Gas Transport in Japan Sea 4,600t/hr
Gas Transport in Japan Sea 4,600t/hr During emergency, for example, by Niigata earthquake accident, the gas delivery to Nagoya and Osaka areas can be secured via Pacific Route.
During emergency, for example, by Niigata earthquake accident, the gas delivery to Nagoya and Osaka areas can be secured via Pacific Route.