Examples on Pipeline Engineering
Pipeline Transport is Best System for Carrying Natural Gas to Customers
- High Efficiency because of No Change into Liquid Phase, Comparing to LNG
- Easy Back-up Supply Possible with Net Work System as in Electric Transmission
- Easy Flow Change Possible with Booster Station ON-OFF System
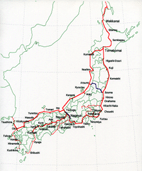 The efficient piepline transporation system is realized by possible high trunkline pressure and possible little pressure loss, however, too large trunkline diameter and too many booster stations are required, resulting in too big initial investment. The appropriate engineering study, therefore, would be indispensable for practical pipeline system establishment. Normally the average pipeline pressure is 6 - 7MPa, and booster station suction/discharge pressures are estimated as 5 - 6MPa, 8 - 9MPa, respectively. In addition, other concepts like multiple pipeline laying to minimize pressure losses can be selected in the case of difficult settlement of booster station due to some reasons.
The efficient piepline transporation system is realized by possible high trunkline pressure and possible little pressure loss, however, too large trunkline diameter and too many booster stations are required, resulting in too big initial investment. The appropriate engineering study, therefore, would be indispensable for practical pipeline system establishment. Normally the average pipeline pressure is 6 - 7MPa, and booster station suction/discharge pressures are estimated as 5 - 6MPa, 8 - 9MPa, respectively. In addition, other concepts like multiple pipeline laying to minimize pressure losses can be selected in the case of difficult settlement of booster station due to some reasons.
This figure shows a typical piepline planning transporting Russian gas to Japan.
Phase 1 Planning shall be Compatible with Future Phase Stages. Pipe sizing, Max. Pressure, Station Locations and etc are Decided.
- On-land Transport in the Northern Regions from Hokkaido, Mainly Off-shore in Others
- On-land Trunkline Size: 1,400mmOD, Maximum Pressure: 7MPa
- Off-shore Trunkline Size: 1,300mmOD, Maximum Pressre: 12MPa
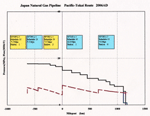 Maximum transport flow is planned as 2,000t/hr, and supplying 700t/hr to metropolitan area. To establish this system, one station outside Hokkaido, two in Hokkaido, and only one in Honshu region are necessary. The appropriate provisions like trunkline headers and bypass line with pig launcher/receiver shall be installed, to avoid future investment savings.
Maximum transport flow is planned as 2,000t/hr, and supplying 700t/hr to metropolitan area. To establish this system, one station outside Hokkaido, two in Hokkaido, and only one in Honshu region are necessary. The appropriate provisions like trunkline headers and bypass line with pig launcher/receiver shall be installed, to avoid future investment savings.
Natural Gas Delivery Rates to Regions
- Hokkaido Region 300t/hr Northeast Region@500t/hr
- East/Metropolitan Region 1,200t/hr
Phase 2 Planning shall be Conducted to Meet Required Regional Gas Demands without Additional Trunkline Laying.
- Additional Installment of Booster Stations
- Adoption of Advanced Aero-GTs to Save Fuel Gas Consumption
- Improvement of Transport Efficiency by Station Cooler/Chiller Installation
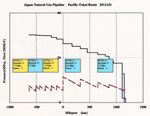 Maximum transport flow is planned as 3,400t/hr, and supplying 1,400t/hr to metropolitan area. Addition of one station outside Hokkaido, three more stations in Hokkaido, and two more staions in Honshu region are necessary. Trunkline size in Tokai looks too large, and this is provisional measure for future tranposrt to Central region, and emergency supply surplus to Western regions.
Maximum transport flow is planned as 3,400t/hr, and supplying 1,400t/hr to metropolitan area. Addition of one station outside Hokkaido, three more stations in Hokkaido, and two more staions in Honshu region are necessary. Trunkline size in Tokai looks too large, and this is provisional measure for future tranposrt to Central region, and emergency supply surplus to Western regions.
Natural Gas Delivery Rates to Regions
- Hokkaido Region 300t/hr Northeast Region@700t/hr
- North Kanto 700t/hr -Metropolitan Region @1,400t/hr
- Tokai@ 300t/hr
 The efficient piepline transporation system is realized by possible high trunkline pressure and possible little pressure loss, however, too large trunkline diameter and too many booster stations are required, resulting in too big initial investment. The appropriate engineering study, therefore, would be indispensable for practical pipeline system establishment. Normally the average pipeline pressure is 6 - 7MPa, and booster station suction/discharge pressures are estimated as 5 - 6MPa, 8 - 9MPa, respectively. In addition, other concepts like multiple pipeline laying to minimize pressure losses can be selected in the case of difficult settlement of booster station due to some reasons.
The efficient piepline transporation system is realized by possible high trunkline pressure and possible little pressure loss, however, too large trunkline diameter and too many booster stations are required, resulting in too big initial investment. The appropriate engineering study, therefore, would be indispensable for practical pipeline system establishment. Normally the average pipeline pressure is 6 - 7MPa, and booster station suction/discharge pressures are estimated as 5 - 6MPa, 8 - 9MPa, respectively. In addition, other concepts like multiple pipeline laying to minimize pressure losses can be selected in the case of difficult settlement of booster station due to some reasons.
 Maximum transport flow is planned as 2,000t/hr, and supplying 700t/hr to metropolitan area. To establish this system, one station outside Hokkaido, two in Hokkaido, and only one in Honshu region are necessary. The appropriate provisions like trunkline headers and bypass line with pig launcher/receiver shall be installed, to avoid future investment savings.
Maximum transport flow is planned as 2,000t/hr, and supplying 700t/hr to metropolitan area. To establish this system, one station outside Hokkaido, two in Hokkaido, and only one in Honshu region are necessary. The appropriate provisions like trunkline headers and bypass line with pig launcher/receiver shall be installed, to avoid future investment savings. Maximum transport flow is planned as 3,400t/hr, and supplying 1,400t/hr to metropolitan area. Addition of one station outside Hokkaido, three more stations in Hokkaido, and two more staions in Honshu region are necessary. Trunkline size in Tokai looks too large, and this is provisional measure for future tranposrt to Central region, and emergency supply surplus to Western regions.
Maximum transport flow is planned as 3,400t/hr, and supplying 1,400t/hr to metropolitan area. Addition of one station outside Hokkaido, three more stations in Hokkaido, and two more staions in Honshu region are necessary. Trunkline size in Tokai looks too large, and this is provisional measure for future tranposrt to Central region, and emergency supply surplus to Western regions.